Astronomie
Scroll down to explore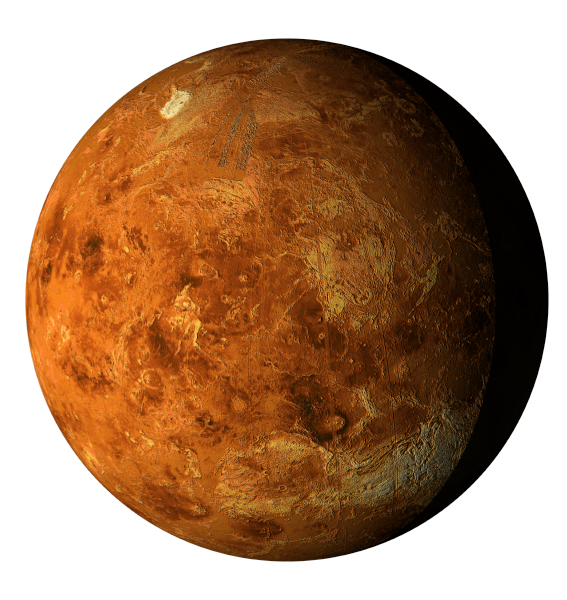
Mercury
The closest planet to the Sun. It has extreme temperatures, ranging from extremely hot to extremely cold. It has a very thin atmosphere and no moons.
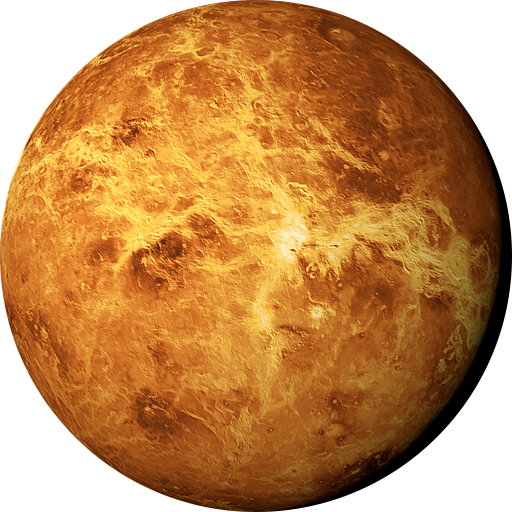
Venus
Similar in size to Earth and often called Earth's "sister planet." Has a thick atmosphere mainly composed of carbon dioxide, causing a runaway greenhouse effect. It rotates on its axis very slowly and in the opposite direction to most planets./p>
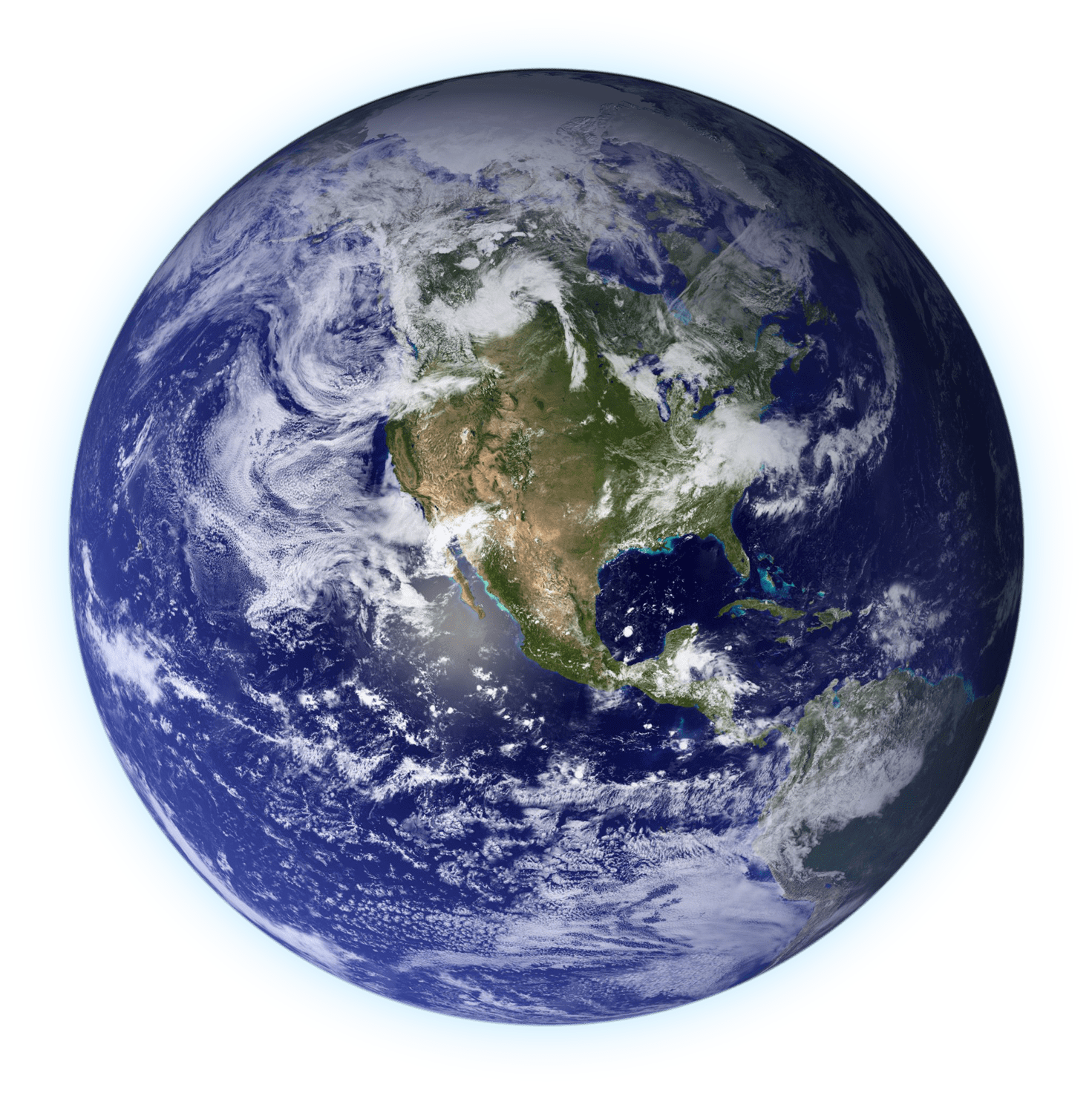

Earth
The only known planet with abundant liquid water on its surface. Supports a diverse range of life forms. The third planet from the Sun.
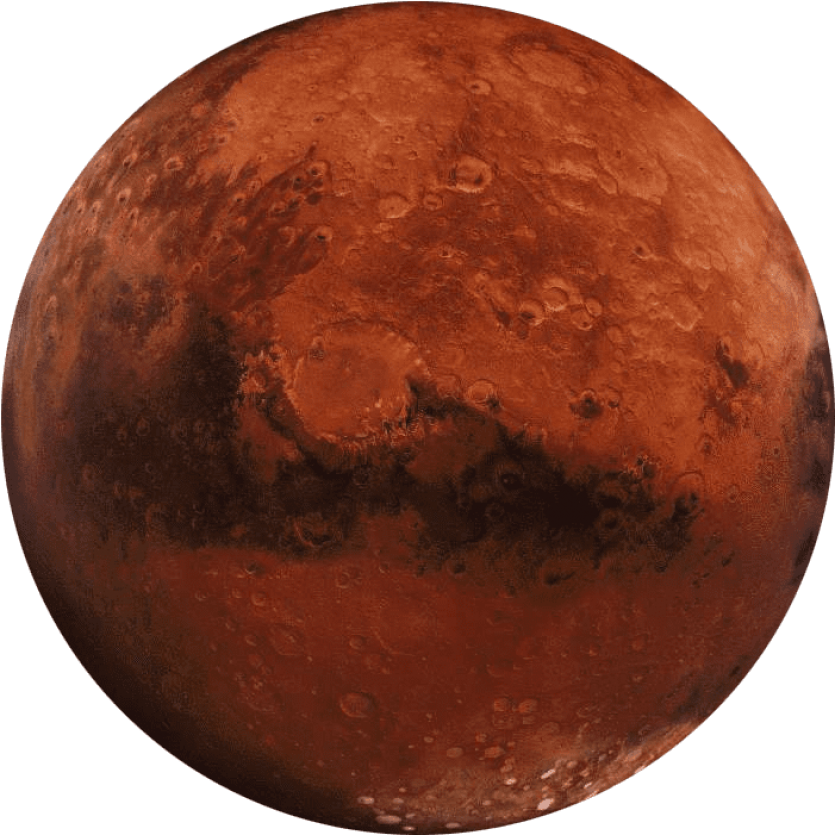

Mars
Often called the "Red Planet" due to its reddish appearance. Has a thin atmosphere composed mostly of carbon dioxide. Contains the tallest volcano and the deepest canyon in the solar system.
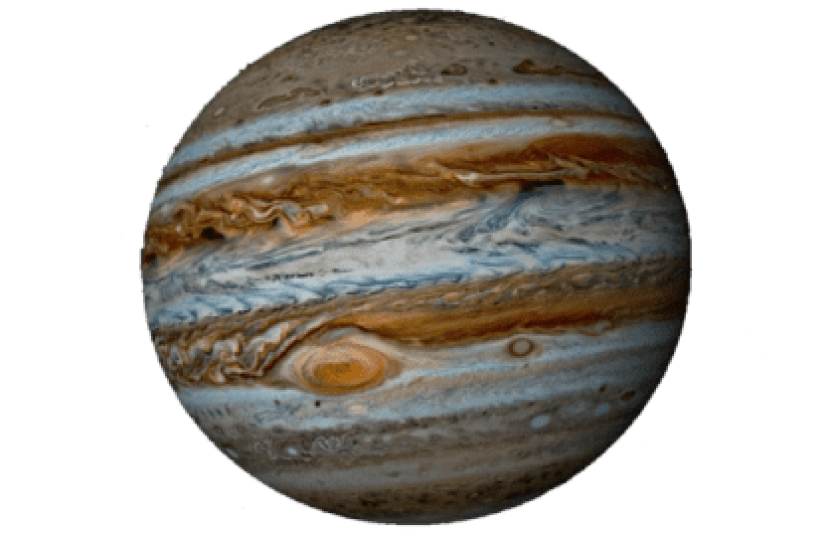

Jupiter
The largest planet in the solar system, primarily composed of hydrogen and helium. Has a strong magnetic field and numerous large moons. The Great Red Spot is a massive storm on Jupiter that has been observed for centuries.
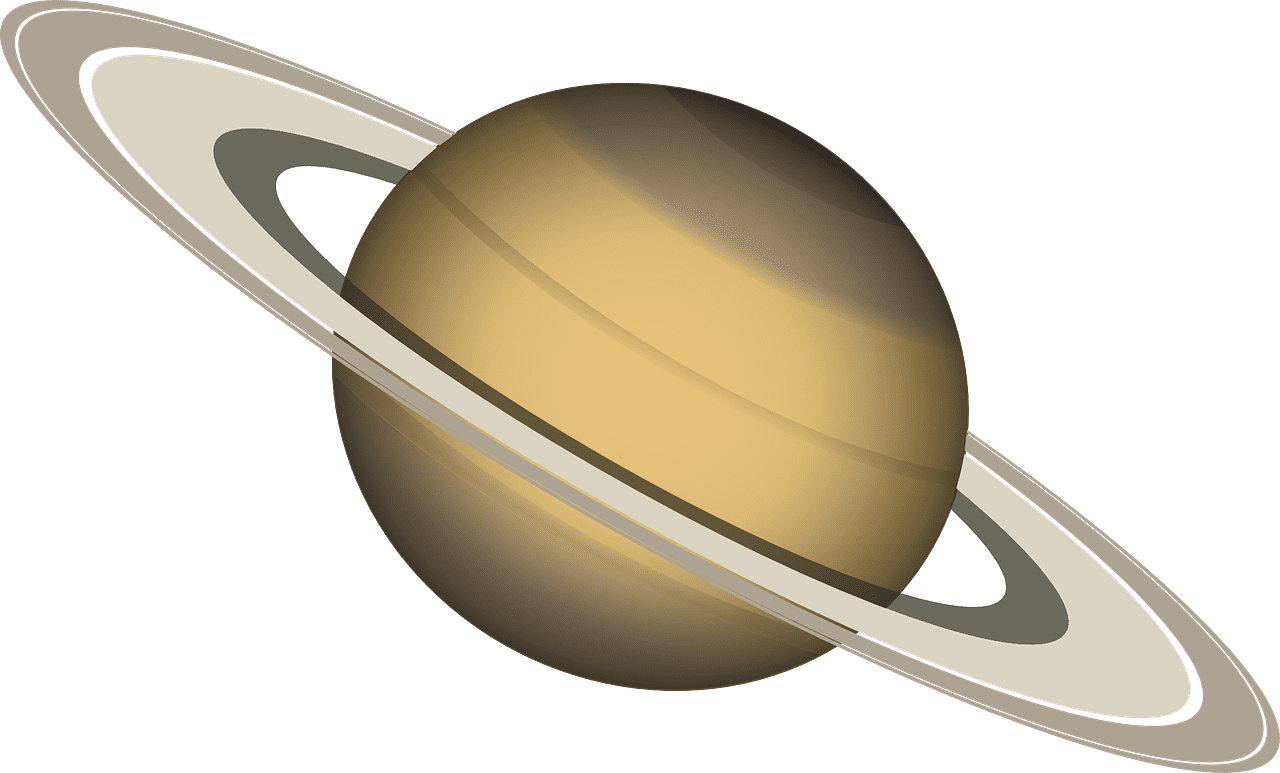
Saturn
Known for its stunning ring system, made up of icy particles and debris. Similar to Jupiter, primarily composed of hydrogen and helium. Has the second-largest moon in the solar system, Titan.
Uranus
A gas giant with a blue-green color due to the presence of methane in its atmosphere. Unique among the planets as it rotates on its side, likely due to a past collision. Has a faint ring system and numerous small moons.v
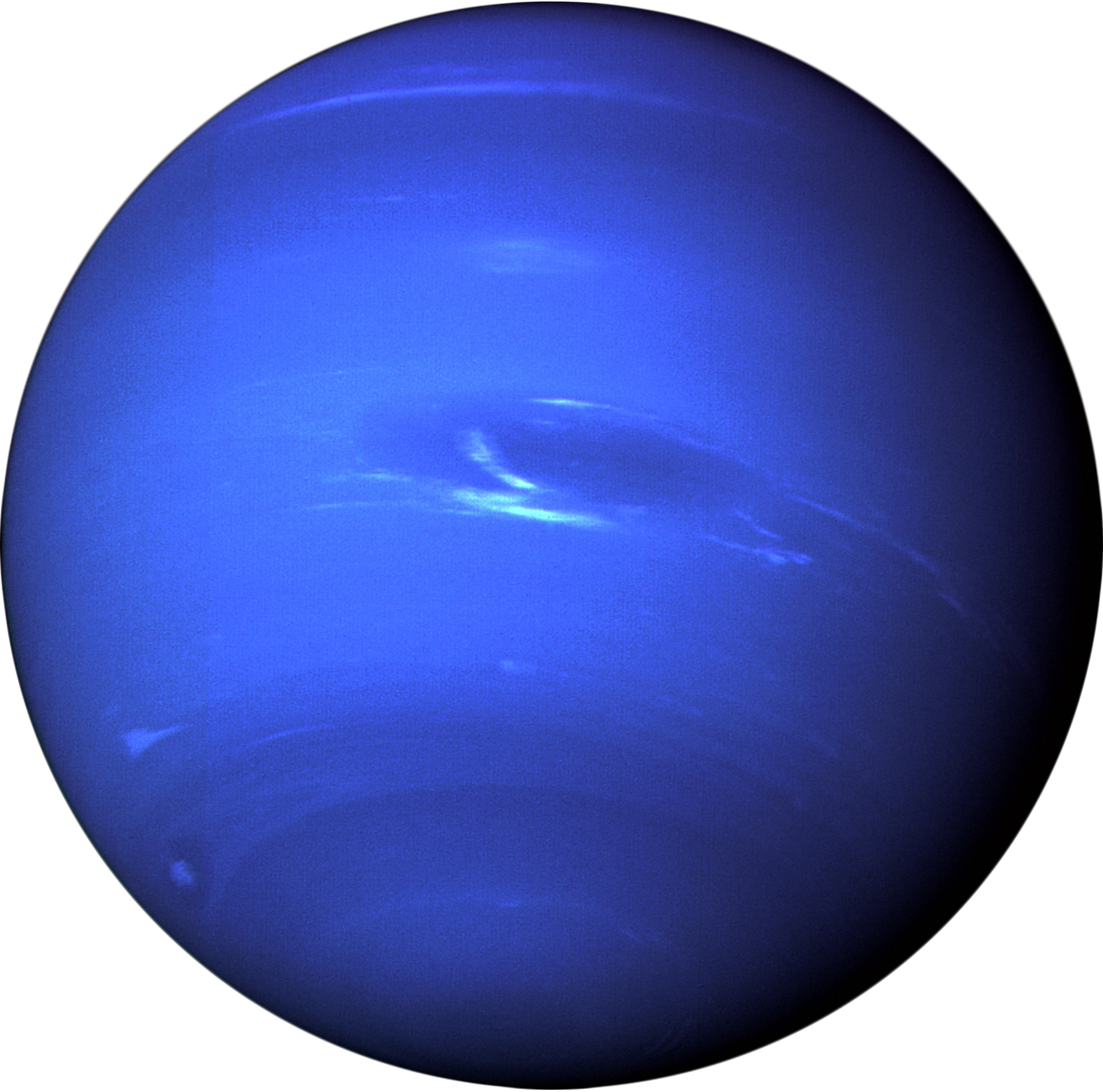
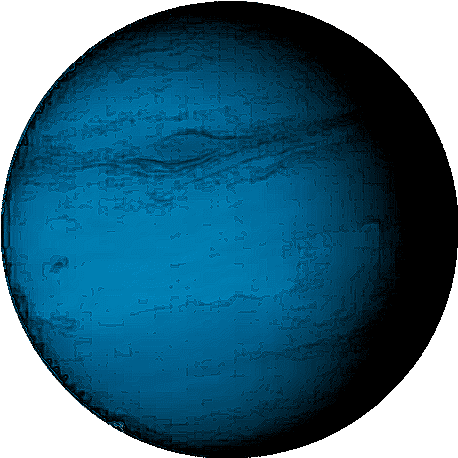
Neptune
The farthest planet from the Sun. Similar in composition to Uranus, with a blue color due to methane in its atmosphere. Has strong winds and a large storm system known as the Great Dark Spot.
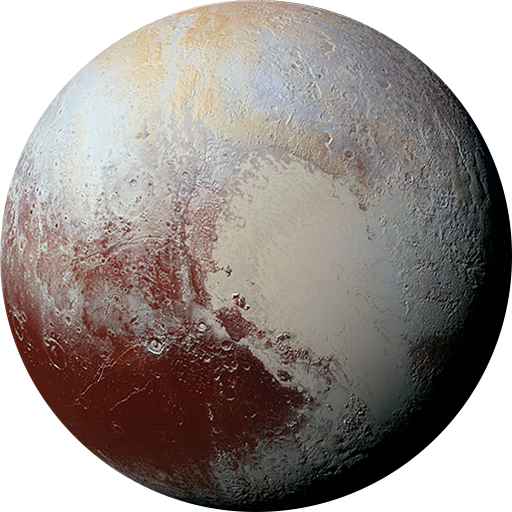

Pluto
Once considered the ninth planet, reclassified as a dwarf planet in 2006. Part of the Kuiper Belt, a region of icy bodies beyond Neptune. Has five known moons, including Charon, which is relatively large compared to Pluto.
